What Are Brain Waves and How Does Our Brain Work?
-
Brain waves are patterns of electrical activity occurring in the brain. They are measured using a technology called Electroencephalography (EEG).
-
There are four main types of brainwaves: delta, theta, alpha, and beta.
-
In specific individuals, brain wave patterns can be dysregulated, and one type of brain wave can dominate too frequently.
-
By using neurofeedback, you can customize brain training to train your brain to reach its optimal state.
The brain is a fascinating, complex organ that controls many aspects of our daily lives. It is responsible for every thought and action, from the deepest philosophical musing to remembering a grocery list to coordinating the motor skills necessary to brush your teeth.
It communicates using electronic signals transferred using neurons, also called brain waves. Brain waves are patterns of electrical activity that can be measured using Electroencephalography (EEG). They can pick up the electric signals from the brain using sensors in the form of metal electrodes.
Brain Wave Frequency Chart: There Are Five Different Types of Brain Waves
Brain waves can be divided into speeds (fast, medium, and slow) and correspond to other thought patterns.
They are often compared to musical notes since each type of brain wave has its own “sound,” distinct from others. When the brain works well, it’s like a symphony in harmony. The different brain waves occur in predictable patterns and use fluid jumps between mental states.
However, the brain wave patterns can be dysregulated in individuals, and one type of brain wave may dominate too frequently.
Brain waves are further broken down into the following three categories based on brainwave frequency:
- Hi-Beta (20.5-28 Hz): Hi-Beta waves are seen during highly complex, rapid thought, including excitement and high anxiety.
- Beta (16.5-20 Hz): Beta waves are intense, focused brain activity occurring when solving a problem or actively engaging with something.
- Lo-Beta (12-16 Hz): Also known as sensorimotor rhythm (or SMR), the Lo-Beta waves reduce anxiety and increase focus.
- Alpha (8-12 Hz): Alpha waves are slower and higher in amplitude than Beta waves and represent a calm, relaxed state. It is the brain’s resting state and occurs during some meditative and mindful activities. Most people can increase their Alpha waves by closing their eyes and taking deep breaths.
- Theta (4-7 Hz): Theta waves are very slow and relate to dreamy, free-flowing, detached unconscious thought. It occurs while doing automatic tasks and sometimes in deep meditative states. It often occurs during dreaming sleep.
- Delta (1 – 3 Hz): Delta waves are low brain waves that occur during dreamless sleep and the deepest meditative states.
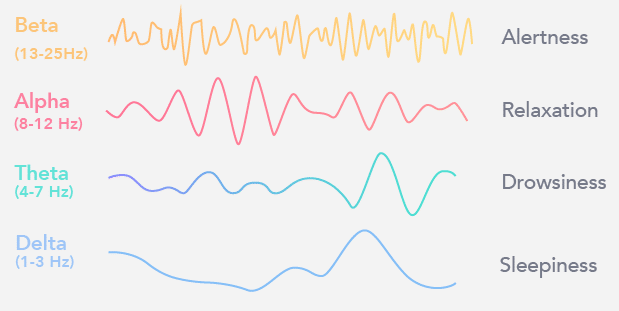
The average person experiences all these brain waves at different times over the day. For instance, their Beta waves would be most active when solving a difficult crossword. They may have more Alpha waves while sitting during a relaxing coffee break. In bed, thinking over the day’s events right before drifting off to sleep, their Theta waves would be dominant.
Is It Possible to Change Your Brainwaves?
With EEG, you can measure your brain wave activity and alter and train your brain to reach its optimal state. This is done through neurofeedback, a noninvasive EEG technology. It uses operant conditioning to train the brain with visual and auditory cues.
It is fun to train with games or videos that respond to your brain wave activity in real-time. Over time, the feedback’s awareness teaches your brain to self-regulate and achieve a healthier, more balanced brain wave state.
As a result of neurofeedback, you can experience improvement in your focus, spatial/motor skills, mood, and overall well-being. You’ll also experience enhancements in different types of memory and attention.
Dr. Trish Leigh provides a personalized, expert-guided brain training program. The program can help you achieve your goals toward improved focus and calm. Check if you’re eligible to kick start your journey with us for better brain health from here.


