Neuro Flow - Peak Performance
Table of Contents
The Key to Peak Performance: Exploring the Characteristics of Flow State
In the dynamic of family life, health, wellness, business, and entrepreneurship, there’s a sweet spot where everything ‘clicks’—this is the flow state, a realm where peak performance isn’t just a goal but a reality. As someone who has navigated the ebb and flow of a large family and a busy profession while serving the community, I’ve experienced firsthand the transformative power of this state. But what if I told you that the secret to unlocking this heightened state of productivity and innovation lies not just in the strategies you implement with your mind and body but in the intricate inner electrical workings of your brain?
My journey through the realms of nurturing a large family and establishing and growing my own business, enriched by a deep fascination with neuroscience, has given me a unique lens through which to view this phenomenon. In the trenches of diapers and deadlines, in the buzz of Zoom meeting rooms, I’ve observed how tapping into the flow state can turn the tide of fortunes. This article isn’t just about the what and how of flow; it’s about integrating the insights of neuroscience to elevate your personal and professional game to levels you’ve only dreamed of.
Let’s dive in and explore how understanding your brain can be your biggest asset in achieving unparalleled performance.

Defining Flow State
What is Flow?
The concept of flow, coined by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, is often described as being 'in the zone.' It's that elusive state where you're completely absorbed in what you're doing, where time seems to stand still, and your productivity skyrockets. You're not just working; you're seamlessly blending with your task, effortlessly riding a wave of focus and creativity. It's like being an equestrian symbiotically, jumping higher and higher posts in synergistic alignment with his horse. Like that equestrian, when you’re in the zone, you control your brain, not vice versa.
The Characteristics of Flow
Flow isn't just a fleeting feeling; it's a state marked by distinct characteristics.

Complete Concentration:
In flow, distractions fade, and focus sharpens as you are highly engaged.

A Sense of Control:
Despite the challenges, you feel a commanding sense of control over the task.
Altered Perception of Time:
Hours might pass like minutes.

Intrinsic Motivation:
What you're doing feels rewarding in itself.

Loss of Self-Consciousness:
You forget yourself, your worries, and your insecurities.

Flow in the Brain:
A Neuroscience Viewpoint
From a neuroscience perspective, flow is a symphony in your brain. When you’re in flow, your prefrontal cortex—the area responsible for higher cognitive functions like self-reflection and planning—takes a backseat. This reduction in activity leads to ‘transient hypofrontality,’ which contributes to the loss of self-consciousness and an altered sense of time. Meanwhile, neurochemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine flood your system, boosting your mood, attention, and pattern recognition abilities.
How to Achieve Neuro Flow Peak Performance
Flow state is elusive, not easily accomplished, for most people. Neuromodulation techniques have been shown by studies to improve brain regulation so as to improve flow state. With improved neuroregulation comes better ability to self regulate. The ultimate self-regulation is flow. It is difficult to get there without brain regulation. The easiest way to come close to flow is by using state-of-the-art technology to faciliate neuroregulation.

Why Flow Matters in Business and Performance
Understanding flow isn't just academic. In business, entering a flow state can mean the difference between average and extraordinary performance. It's about harnessing your brain's natural capabilities to supercharge your productivity and creativity. Whether you're solving complex problems, brainstorming new ideas, or making critical decisions, tapping into flow can elevate your work from mundane to exceptional.
The Business of Flow
In the high-stakes arena of corporate business, flow becomes more than just a personal experience; it’s a powerful tool that can reshape entire organizations. Imagine teams where every member is deeply engaged, where meetings and projects are not just productive but invigorating, and where solutions to complex problems emerge almost effortlessly. This isn’t wishful thinking – it’s the practical application of flow in a corporate setting and can be achieved when all team members are neurologically regulated. Technology can help your team achieve flow.
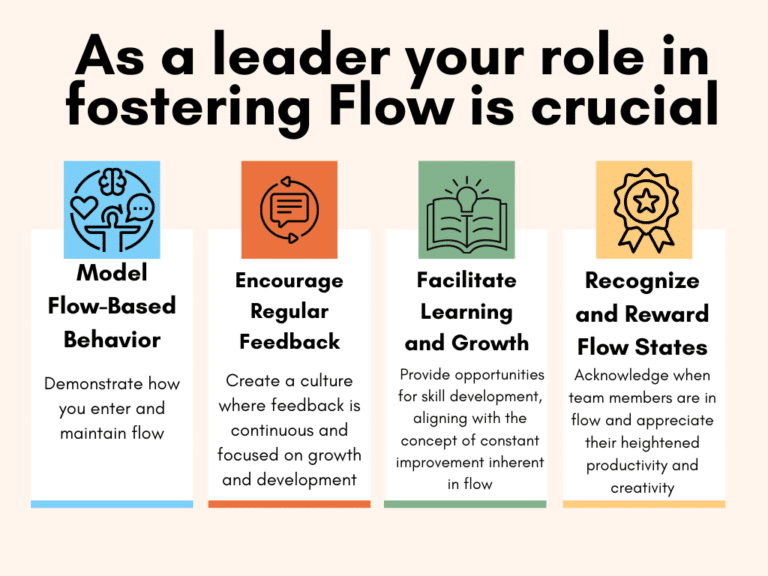
Flow and Personal Leadership
As a leader, embodying the principles of flow in your work can set a powerful example. Show your team how to balance stress and relaxation, demonstrate deep focus, and maintain a growth mindset. Your approach to challenges and learning can inspire your team to seek their flow states.
The Neuroscience Behind Flow
A deeper dive into its neurological underpinnings is crucial to harness the power of flow in the business world. Understanding what happens in our brains during flow can help us replicate these conditions more effectively in our professional lives.
The Brain’s Symphony in Flow
When you enter flow, your brain is not quiet, but it’s not in overdrive either. It’s more like it’s playing a well-orchestrated symphony. Key areas involved include:
The Prefrontal Cortex
This area, associated with cognitive functions like planning and self-reflection, shows decreased activity in flow, leading to reduced self-doubt and distraction.
The Limbic System
Involved in emotion processing, this system helps generate the pleasure we associate with flow.
The Release of Neurochemicals
Dopamine, norepinephrine, endorphins, anandamide, and serotonin flood the system, enhancing focus, creativity, and learning.
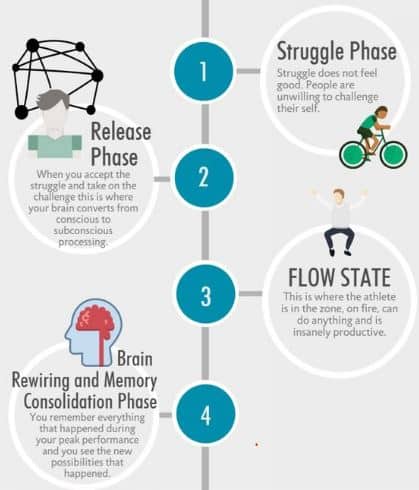
Transient Hypofrontality: The Science of ‘Losing Yourself’
This phenomenon, where the prefrontal cortex temporarily down-regulates, is central to the flow experience. It results in a feeling of time distortion, loss of self-consciousness, and heightened concentration. Essentially, it’s your brain’s way of removing internal barriers and allowing you to focus intensely on the task at hand.

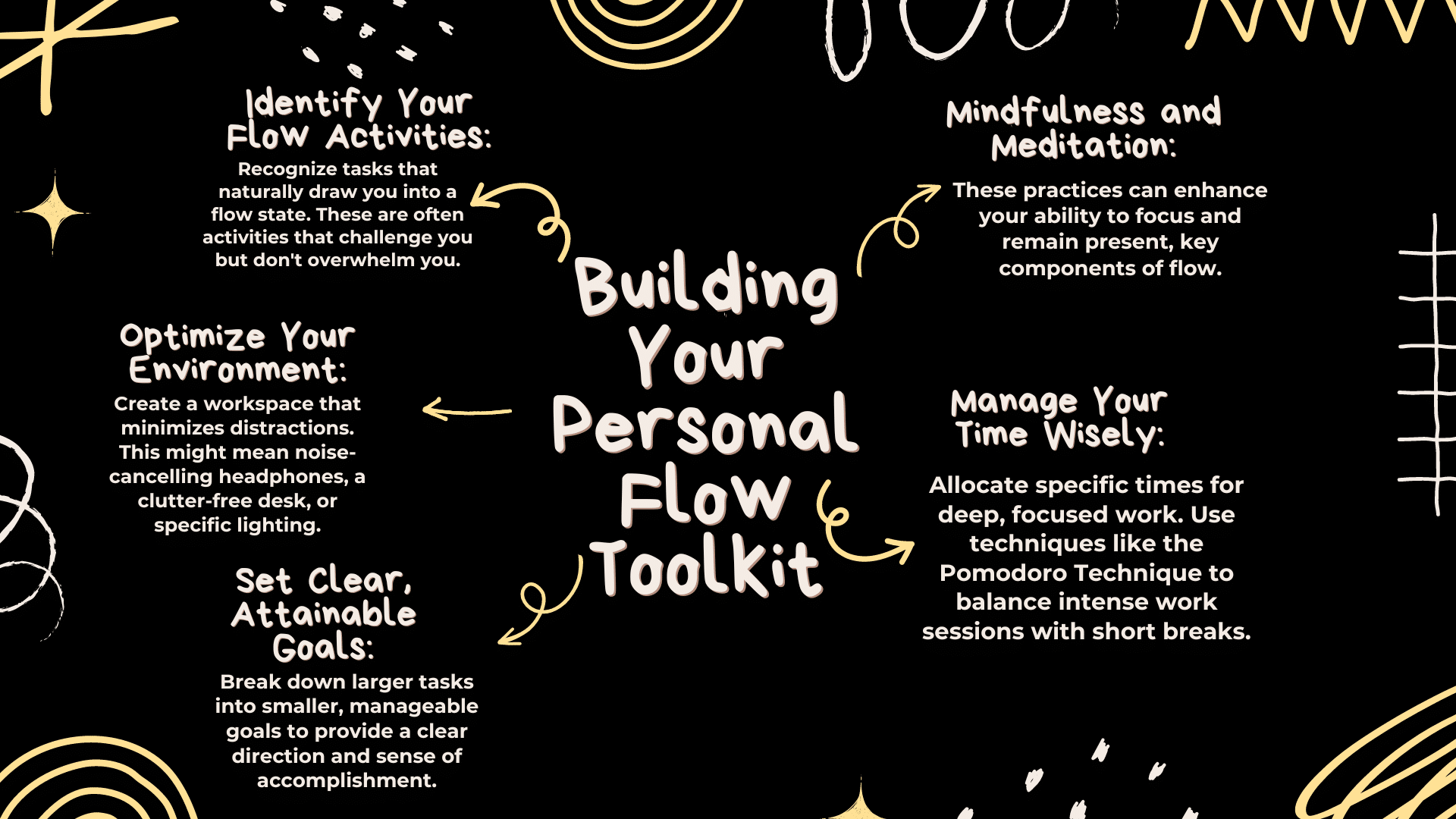
Cultivating Flow - Techniques and Strategies
To consistently achieve a flow state, you need a personal toolkit tailored to your brain’s wiring and work style. Here are some strategies:

Overcoming Obstacles to Flow
Identifying Barriers to Flow. It's important to recognize and mitigate common obstacles to flow:
Distractions:
Minimize external interruptions and encourage self-discipline.
Burnout:
Balance workloads and stress the importance of rest and recovery.
Poor Team Dynamics:
Lack of trust, unclear communication, and unresolved conflicts can disrupt the flow in team settings.
Lack of Direction:
Provide clear objectives and expectations.
Neurological Dysregulation:
When one or more team members is neurologically dysregulated this can be enough to hinder flow for the whole team. Technology can help team members self-regulate.
Stress:
Excessive stress can impede the brain’s ability to enter flow, while burnout can make it almost impossible.
Strategies to Overcome These Barriers:
- Encourage practices like ‘deep work’ hours where interruptions are minimized. Use technology mindfully – set specific times to check emails and messages.
- Regularly assess and realign tasks with individual skills and growth edges. This balance is key to maintaining the challenge-skill equilibrium necessary for flow.
- Build a culture of open communication, trust, and respect. Regular team-building activities and open forums can strengthen team dynamics.
- Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, regular breaks, and physical activities into the work routine. Recognize the signs of burnout and take proactive steps to address it.
The Impact of Flow in Long-term Success
Incorporating flow into your business strategy can yield significant long-term benefits:
- Enhanced Productivity and Innovation: Regular flow states lead to higher productivity and more innovative solutions, giving your business a competitive edge.
- Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Flow contributes to job satisfaction, as employees feel more engaged and accomplished, leading to lower turnover rates.
- Agility and Adaptability: Teams accustomed to flow are better equipped to adapt to change, a crucial attribute in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Encouraging Team Flow
Achieving flow in a team setting can amplify results significantly.

Here’s how to cultivate it:
Clear Shared
Goals:
Ensure that everyone understands and is aligned with the team's objectives.
Autonomy
and
Mastery:
Give team members control over their work and opportunities to use their strengths.
Open
Communication:
Foster an environment where ideas can be freely shared and feedback is constructive.
Sustaining Flow for Enduring Achievement
Achieving flow occasionally is beneficial, but the magic happens when it becomes a regular part of your professional life. Sustaining flow can lead to continuous improvement, increased productivity, and long-term success.
Here’s how to maintain it:
- Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth.
-
Regular Reflection and Adaptation: Periodically reflect on your flow experiences. What worked? What didn't? Adapt your strategies accordingly to keep the flow fresh and effective.
- Lifelong Learning: Continuously update your skills and knowledge. This keeps the challenge-skill balance in check, which is essential for flow.
Evaluate What Your Brain Needs to Achieve Neuro Flow:
What is Flow?
The concept of flow, coined by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, is often described as being 'in the zone.' It's that elusive state where you're completely absorbed in what you're doing, where time seems to stand still, and your productivity skyrockets. You're not just working; you're seamlessly blending with your task, effortlessly riding a wave of focus and creativity. It's like being an equestrian symbiotically, jumping higher and higher posts in synergistic alignment with his horse. Like that equestrian, when you’re in the zone, you control your brain and not vice versa.
The Characteristics of Flow
From a neuroscience perspective, flow is a symphony in your brain. When you're in flow, your prefrontal cortex – the area responsible for higher cognitive functions like self-reflection and planning – takes a backseat. This reduction in activity leads to 'transient hypofrontality,' which contributes to the loss of self-consciousness and altered sense of time. Meanwhile, neurochemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine flood your system, boosting your mood, attention, and pattern recognition abilities.
Flow isn't just a fleeting feeling; it's a state marked by distinct characteristics:

Complete Concentration:
In flow, distractions fade, and focus sharpens as you are highly engaged.

A Sense of Control:
Despite the challenges, you feel a commanding sense of control over the task.

Altered Perception of Time:
Hours might pass like minutes.

Intrinsic Motivation:
What you're doing feels rewarding in itself.

Loss of Self-Consciousness:
You forget yourself, your worries, and your insecurities.

Flow in the Brain:
A Neuroscience Viewpoint
Neurofeedback Brain Training to Achieve Flow.
Flow state is elusive, not easily accomplished, for most people. Neuromodulation techniques have been shown by studies to improve brain regulation so as to improve flow state. With improved neuroregulation comes better ability to self regulate. The ultimate self-regulation is flow. It is difficult to get there without brain regulation. The easiest way to come close to flow is by using state-of-the-art technology to faciliate neuroregulation.
Flow and Team Evolution
- Evolving Team Dynamics: As the team grows and changes, so should your approach to fostering flow. Regularly reassess team goals, roles, and dynamics.
- Building a Resilient Team Culture: Encourage a culture where learning from failures and successes is the norm. This resilience is key to maintaining flow in the face of challenges.
Sustaining flow is not a one-time effort; it’s a continuous journey. It requires commitment, adaptability, and a deep understanding of yourself and your team. By making flow a central part of your professional life, you’re not just enhancing it you are..
Unleashing the Power of Flow in Your Professional Journey
As we wrap up this exploration into the realm of flow, it’s clear that this state is much more than a fleeting moment of clarity or a burst of productivity. Flow is a powerful, transformative experience that, when harnessed effectively, can catapult individuals and organizations to unprecedented heights of performance and success.
Summary
Reflecting on our journey through the various facets of flow, we’ve uncovered not just the what and the how, but also the why. We’ve delved into the neuroscience behind flow, understanding how our brains orchestrate this state, and we’ve explored practical strategies to invite this state into our daily professional lives. We’ve tackled the challenges and obstacles hindering flow and discussed ways to overcome them.
As a guide in the intertwining paths of business and neuroscience, I’ve witnessed the remarkable changes that flow can bring. It’s not just about working harder or longer; it’s about working smarter, tapping into the depths of our cognitive and creative resources. It’s about aligning our work with our brain’s natural rhythms and capabilities.
Remember, achieving and sustaining flow is a journey. The easiest and fastest way to achieve flow is through It’s a process of continuous learning, adaptation, and growth. As you apply these insights and strategies, be patient with yourself and your teams. Celebrate the small wins, learn from the challenges, and keep pushing the boundaries of what you thought possible.
Ultimately, the journey to mastering flow is as enriching as the outcomes it yields. It’s about finding that sweet spot where your skills, challenges, and passions meet, leading to peak performance and a more fulfilling professional life. So, embrace this journey, and let the power of flow unlock your true potential.
Don’t hesitate to reach out if you’re looking for more personalized advice or coaching on integrating flow into your professional life. I’m here to guide you on this journey, combining insights from the worlds of business and neuroscience to unlock your peak performance.

